Total chemical synthesis and X-ray structure of kaliotoxin by racemic protein crystallography
By Brad L Pentelute, Kalyaneswar Mandal, Zachary P Gates, Michael R Sawaya, Todd O Yeates, and Steve Kent
Published in Chemical communications (Cambridge, England) 46(43): 8174-6 on Nov. 21, 2010.
PMID: 20877851. Link to Pubmed page.
Core Facility: Membrane Protein Expression/Purification
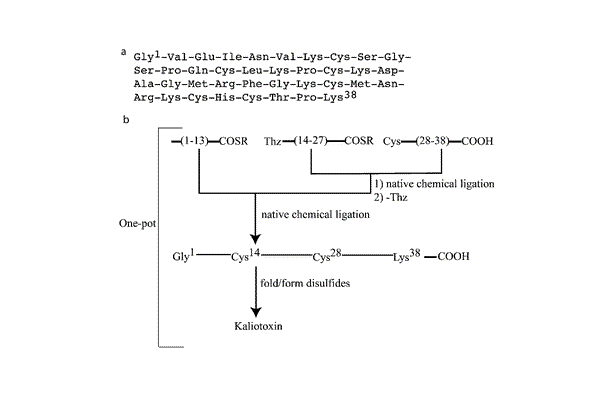
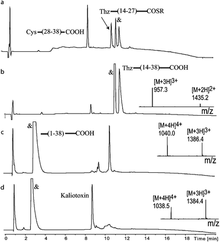
Figure 1. (a) The 38-residue amino acid sequence of kaliotoxin. (b) The modular three segment one-pot ligation strategy for the total chemical synthesis of kaliotoxin. The first native chemical ligation step is followed by the conversion of the N -terminal 1,3-thiazolidine-4-R-carboxylic acid (Thz) to Cys. After the second native chemical ligation, the full-length polypeptide is folded with concomitant formation of the three native disulfide bonds.
Abstract
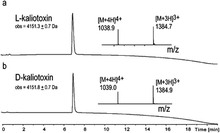
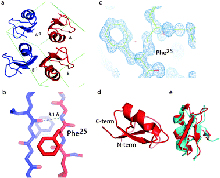
Here we report the total synthesis of kaliotoxin by ‘one pot’ native chemical ligation of three synthetic peptides. A racemic mixture of D- and L-kaliotoxin synthetic protein molecules gave crystals in the centrosymmetric space group P1 that diffracted to atomic-resolution (0.95 Å), enabling the X-ray structure of kaliotoxin to be determined by direct methods.