Applications for an engineered Protein-G variant with a pH controllable affinity to antibody fragments
By Lucas J. Bailey, Kimberly M. Sheehy, Robert J. Hoey, Zachary P. Schaefer, Marcin Ura, and Anthony A. Kossiakoff.
Published in J Immunol Methods, 2014 Dec 15;415:24-30.
PMID: 25450256. PMCID: PMC4257880. Link to publication page.
Core Facility: Synthetic Antigen Binder (SAB) Generation and Crystallography
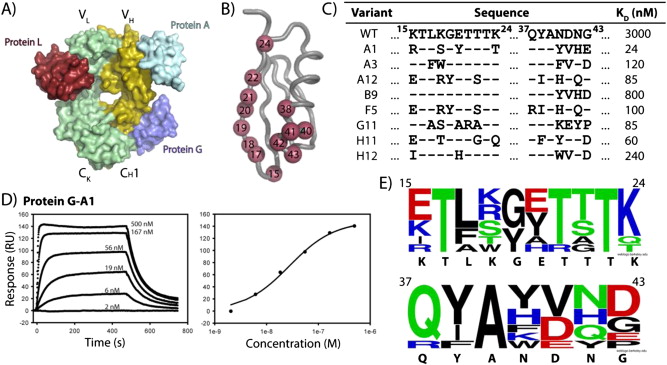
Figure 1. Engineering of Protein-G. A). Binding epitopes of immunoglobulin proteins on the antibody fragment. B). Residues randomized on Protein-G are represented as red spheres. C). Resulting sequences of engineered Protein-G variants with improved affinity for the human antibody fragment. Affinities were determined by equilibrium SPR. D). Equilibrium SPR sensogram and binding isotherm of the Protein-G-A1 variant. E). WebLogo plot of the amino acid frequencies of randomized positions in engineered Protein-G variants from 1C.
Abstract
Immunoglobulin binding proteins (IBPs) are broadly used as reagents for the purification and detection of antibodies. Among the IBPs, the most widely used are Protein-A and Protein-G. The C2 domain of Protein-G from Streptococcus is a multi-specific protein domain; it possesses a high affinity (K(D) ~10 nM) for the Fc region of the IgG, but a much lower affinity (KD~low μM) for the constant domain of the antibody fragment (Fab), which limits some of its applications. Here, we describe the engineering of the Protein-G interface using phage display to create Protein-G-A1, a variant with 8 point mutations and an approximately 100-fold improved affinity over the parent domain for the 4D5 Fab scaffold. Protein-G-A1 is capable of robust binding to Fab fragments for numerous applications. Furthermore, we isolated a variant with pH-dependent affinity, demonstrating a 1,000-fold change in affinity from pH7 to 4. Additional rational mutagenesis endowed Protein-G with significantly enhanced stability in basic conditions relative to the parent domain while maintaining high affinity to the Fab. This property is particularly useful to regenerate Protein-G affinity columns. Lastly, the affinity-matured Protein-G-A1 variant was tethered together to produce dimers capable of providing multivalent affinity enhancement to a low affinity antibody fragment-antigen interaction. Engineered Protein-G variants should find widespread application in the use of Fab-based affinity reagents.


