De novo mutation in the dopamine transporter gene associates dopamine dysfunction with autism spectrum disorder
By P J Hamilton, N G Campbell, S Sharma, K Erreger, F Herborg Hansen, C Saunders, A N Belovich, NIH ARRA Autism Sequencing Consortium: M J Daly, R A Gibbs, E Boerwinkle, J D Buxbaum, E H Cook, B Devlin, E T Lim, B M Neale, K Roeder, A Sabo, G D Schellenberg, C Stevens and J S Sutcliffe; M A Sahai, E H Cook, U Gether, H S Mchaourab, H J G Matthies, J S Sutcliffe and A Galli.
Published in Molecular Psychiatry [Epub ahead of print] on August 27, 2013. PMID: 23979605. Link to publication page.
Project: The Transport Cycle in Neurotransmitter Uptake Systems
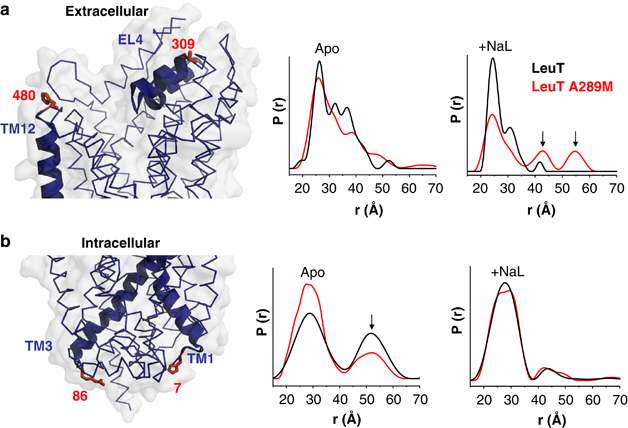
Figure 4. In leucine transporter (LeuT), substitution of Ala289 with a Met supports an outward-open facing conformation. Distance distributions of extracellular and intracellular spin labeled Cys pairs in LeuT reveal changes in the conformational equilibrium caused by mutating Ala289 to a Met. (a) Left: extracellular reporter pairs (309–480) tagged on three-dimensional structure of LeuT. Right: distance of the extracellular reporter pair for LeuT (black) and A289M (red), in the Apo conformation (Apo) and in the presence of Na+ and Leu (+NaL). (b) Left: intracellular reporter pairs (7–86) tagged on the three-dimensional structure of LeuT. Right: distance of the intracellular reporter pair for LeuT (black) and A289M (red), in the Apo conformation (Apo) and in the presence of Na+ and Leu (+NaL). The LeuT structure was obtained from PDB 2A65. The structures were generated using PyMOL.
Abstract
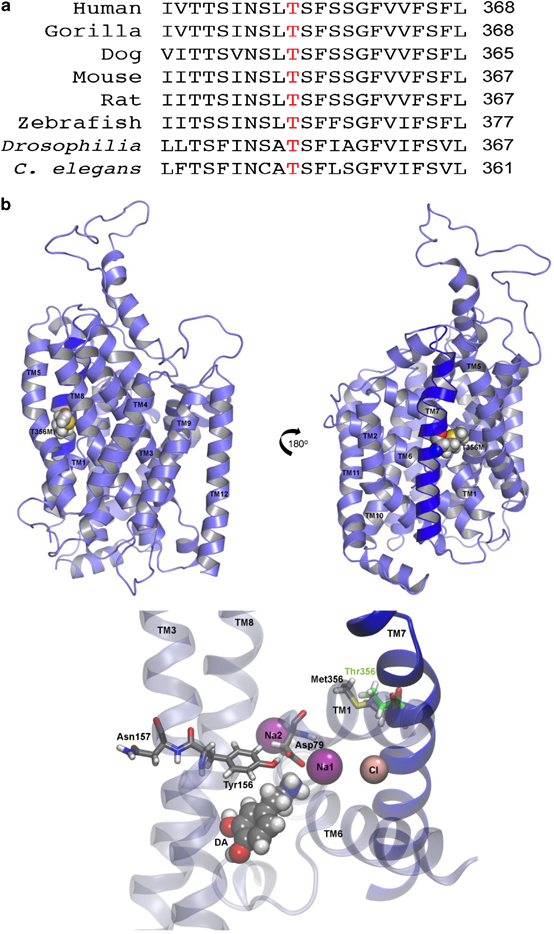
De novo genetic variation is an important class of risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Recently, whole-exome sequencing of ASD families has identified a novel de novo missense mutation in the human dopamine (DA) transporter (hDAT) gene, which results in a Thr to Met substitution at site 356 (hDAT T356M). The dopamine transporter (DAT) is a presynaptic membrane protein that regulates dopaminergic tone in the central nervous system by mediating the high-affinity reuptake of synaptically released DA, making it a crucial regulator of DA homeostasis. Here, we report the first functional, structural and behavioral characterization of an ASD-associated de novo mutation in the hDAT. We demonstrate that the hDAT T356M displays anomalous function, characterized as a persistent reverse transport of DA (substrate efflux). Importantly, in the bacterial homolog leucine transporter, substitution of A289 (the homologous site to T356) with a Met promotes an outward-facing conformation upon substrate binding. In the substrate-bound state, an outward-facing transporter conformation is required for substrate efflux. In Drosophila melanogaster, the expression of hDAT T356M in DA neurons-lacking Drosophila DAT leads to hyperlocomotion, a trait associated with DA dysfunction and ASD. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that alterations in DA homeostasis, mediated by aberrant DAT function, may confer risk for ASD and related neuropsychiatric conditions.

![Figure 2. Human dopamine transporter (hDAT) T356M has impaired function. (a) Top: kinetic parameters (Vmax and Km) for hDAT and hDAT T356M (Vmax: Pless than or equal to0.005; by Student’s t-test; n=3, in triplicate; Km: Pgreater than or equal to0.20; by Student’s t-test; n=3, in triplicate). Bottom: representative plot of [3H]DA uptake kinetics in hDAT (filled squares) or hDAT T356M (empty squares) cells (**=Pless than or equal to0.01, ***=Pless than or equal to0.001; by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni post-test; n=3, in triplicate). (b) Representative immunoblots for biotinylated (surface) and total protein fractions from hDAT and hDAT T356M cells. Surface fractions were quantitated, normalized to total DAT (glycosylated) and expressed as a percent of hDAT (Pgreater than or equal to0.05; by Student’s t-test; n=8–11).](/site-media/images/publications/2013/mchaourab-2013-figure2.jpg)